Global / Centralized Procurement
In a multi-org environment, many a times
business demands centralize procurement across multiple operating units as this
provides following major benefits
1.Provides cost savings by consolidating purchases
for volume discounts
2. Centralized control provides a single source of
information for businesses
3. Better control on purchasing is possible under
centralized purchasing. There is no chance of reckless purchase since one unit
is authorized to make purchase for the whole organization.
Business
Flow Demonstrated in this White Paper:
Step1:
Creation of Requisition from Operating X (ZZ Plant)
Step
2: Creation of Purchase order in Centralized Operating Unit Y (Vision
Operations)
Step3: Receiving in Inventory Organization (ZA1) which
belongs to Operating Unite X (ZZ Plant)
Step4: Request for Intercompany Invoice Generation
Mandatory setup:
1.
Setup Following profile options
INV: Intercompany Invoice for Internal Orders = Yes
CST: Transfer Pricing Option = Yes, Price Not As
Incoming Cost
2.
Make sure your Security profiles setup provide
access to all the Organizations involved in Purchasing Process.
Make Sure Centralized Operating Unit should also be
defined as Logical Inventory organization.
Make Sure Purchasing Item access is been given to
all inventory organizations involved in Global procurement Process. (This
includes the Logical inventory organization also)
3:
Creation of Internal Customer
4.
Creation of
Intercompany Transactions Flow:
Setup> Organizations> Intercompany Transaction
Flows
(Note: ‘Start’ should be ‘Procuring Organization’.
End should be operating Unit of ‘Receiving Inventory’ organization.)
Transaction
Flow:
Step1:
Create
Requisition
(Note: Operating unit will be the Requesting
operating unit , Organization should be the Inventory organization within a
requesting OU where you would like to receive material)
Step2:
Approve
requisition
Step3: Create PO in
Centralized OU which will be buying on behalf of other OU’s
Responsibility:
Purchasing Super User
Navigation:
Autocreate> Find out the requisition that needs to be processed
Click on ‘Automatic’ Button. Most
Important: Select Centralized OU (In our case ‘Vision Operations’) as a
Purchasing Org.
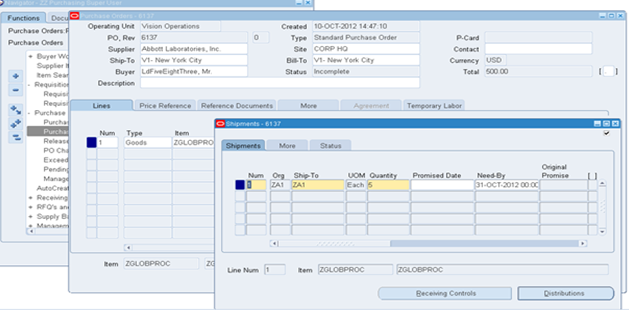
Step4:
Provide Ship-to and Bill-to Details at PO Header, Verify details , Check
Shipment level details, Initiate PO Approval.
Step5:
Receive Material in requesting Inventory Organization










Comments
Post a Comment