Planning and forecast functionality in iSupplier Portal.
Basic objective of this whitepaper is
>Identifying
a key setups to complete Demand planning to supply flow
>Identifying
the role of advanced modules like ASCP to achieve better execution of Supplier scheduling
process
>Basic
flow of ASCP
Setup
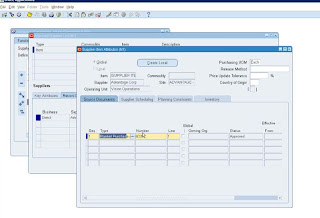
Step 1: Item creation
Note: Item should be ‘Purchased’ and ‘Purchasable’
enabled. Ensure ‘planner’ is entered under general planning tab (At organization level) Ensure it’s a
‘Buy’ item.
In the MPS/MRP Planning tab - the item should have a planning method
- MRP Planning (Or method of planning used at the Location)
- Create Supply
Step7: Run ASCP Data Collection (From Advanced Supply Chain Planner)
Step11: Execute Push Plan (From Advanced Supply Chain planner Responsibility)
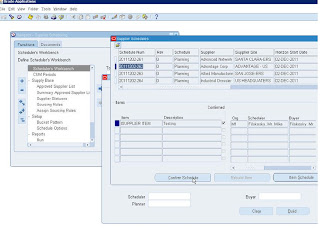
Responsibility : Supplier Scheduling
Generate Schedules and Confirm schedules.. Once schedule line is confirmed it will display in iSupplier
View Data in iSupplier Portal


















Comments
Post a Comment